Our Environment
The ecosystem is the structural and functional unit of ecology where the living organisms interact with each other and the surrounding environment.
An ecosystem is a chain of interactions between organisms and their environment.
During this biological process, light energy is converted into chemical energy and is passed on through successive levels. The flow of energy from a producer, to a consumer and eventually, to an apex predator or a detritivore is called the food chain.
The structure of an ecosystem is characterised by the organisation of both biotic and abiotic components. This includes the distribution of energy in our environment. It also includes the climatic conditions prevailing in that particular environment.
The ecosystem is the structural and functional unit of ecology where the living organisms interact with each other and the surrounding environment.
An ecosystem is a chain of interactions between organisms and their environment.
Types of ecosystem:
An ecosystem can be as small as an oasis in a desert, or as big as an ocean, spanning thousands of miles.
1. A terrestrial ecosystem is a land-based community of organisms and the interactions of biotic and abiotic components in a given area. They are as follows:
2. A forest is an area of land dominated by trees and animals that live in coordination with the abiotic factors of the environment.
3. In a grassland ecosystem, the vegetation is dominated by grasses and herbs.
4. In physical geography, tundra is a type of biome where the tree growth is hindered by low temperatures and short growing seasons.
In physical geography, tundra is a type of biome where the tree growth is hindered by low temperatures and short growing seasons.
Aquatic ecosystems are ecosystems present in a body of water. These can be further divided into two types, namely:
The freshwater ecosystem is an aquatic ecosystem that includes lakes, ponds, rivers, streams and wetlands. These have no salt content in contrast with the marine ecosystem.
The marine ecosystem includes seas and oceans. These have a more substantial salt content and greater biodiversity in comparison to the freshwater ecosystem.
The structure of an ecosystem is characterised by the organisation of both biotic and abiotic components. This includes the distribution of energy in our environment. It also includes the climatic conditions prevailing in that particular environment.
FUNCTIONS OF THE ECOSYSTEM:
It regulates the essential ecological processes, supports life systems and renders stability.
It is also responsible for the cycling of nutrients between biotic and abiotic components.
It maintains a balance among the various trophic levels in the ecosystem.
It cycles the minerals through the biosphere.
The abiotic components help in the synthesis of organic components that involves the exchange of energy.
During this biological process, light energy is converted into chemical energy and is passed on through successive levels. The flow of energy from a producer, to a consumer and eventually, to an apex predator or a detritivore is called the food chain.
Chapter- 1
Grade- 5
Q.1. For which one do animals depend on plants?
Ans: Animals depend on plants for food.
Q.2. What is ecosystem?
Ans: All living and non-living things that exist and interact in one place is called an ecosystem.Q.3. What is pollination?
Ans: Transfer of pollen from one flower to another flower so that plants can make seeds.Q.4. What is food web?
Ans: Several food chains connecting together make a food web.
Q.5. What are the differences between food chain and food web?
Ans: Differences between food chain and food web are :
1. The path of food energy in an ecosystem from plants to animals is called food chain.
1. Several food chains connected together are called a food web.
2. It establishes the relationship between different plants and animals.
2. It indicates the relationship between different food chains.
3. Food chain begins with the green plants.
3. Food web does not begin with any specific elements.
4. In an ecosystem, several food chains can exist.
4. In an ecosystem only one food web can exist.
5. Eater, factors and disjunctives may not exist together.
5. Eater, factors and disjunctives exist together.
Q.6. Why seed dispersal is important for plants?
Ans: Seed dispersal means the transport of seeds away from the parent plant. It is very important for plants because it helps create new colonies for plants. If it does not occur properly, animals including humans will suffer from scarcity of food and shelter. As a result, the balance of biodiversity will be hampered. Besides, if seed dispersal does not take place properly, large number of plants of some species will grow at the same place. Eventually, nutrition of other plants will be hampered.Q.7. Describe the correct sequence of food chain that has the following things: Eagle, grasses, insects, snake, frog.
Ans: The correct sequence of food chain that has eagle, grasses, insects, snake and frog is: Grasses insects frog snake eagle Explanation: The sun is the source of all energy. Grass produces its own food by using the energy of the sunlight. Insects live on grasses. Again, frog takes insects as food. In the same way, snake eats frog, and eagle eats snake. In this way, energy flows from grasses to eagle.Q.8. What is the main source of energy?
Ans: Sun is the main source of energy.Q.9. What is mutual dependency?
Ans: Any interdependent or mutually beneficial relationship between two persons, groups etc. is called mutual dependency.Environmental Pollution
Chapter-2
2. Short Q/A
Q.1. What is the environmental pollution?
Ans: Our environment changes in many ways. When the changes are harmful to the living things, it is called environmental pollution.
Q.2. What are the effects of air pollution?
Ans: The effects of air pollution are—
i) Global warming
ii) Acid rain
iii) Respiratory diseases like lung cancer, bronchitis etc.
Q. 3. Write down the ways of environmental pollution?
Ans: The ways of environmental pollution are-i) Use of pesticides and fertilisers in agricultureii) Harmful gases into the air.Q.4. What are the sources of environmental pollution?
Ans: The main sources of environmental pollution are the burning of fossil fuels, industrialization, population growth, toxic chemical and household waste.
Q.5. Write the five ways of environmental conservation.
Ans: The five ways of environmental conservation are- Wise use Dumping garbage in the dustbin Planting trees Raising public awareness Reusing of natural resources.
3. Descriptive Answer questions.
1) Explain the harmful effects of environmental pollution.
Ans: The harmful effects of environmental pollution are- Destruction of their habitats Animals get extinct Sea level rise Global warming People sick with lung cancer, and respiratory diseases.2) What is noise pollution? What is the harmful impact of noise pollution?
Ans: Noise pollution is sound in the environment that harms the health of human or animal life. Noise pollution has severe mental and physical effect on human health. Depression, hearing loss, sleep disruption and loss of productivity are caused by noise pollution.3) What is environmental conservation? How can we conserve our environment?
Ans: Environmental conservation is the sustainable and wise use and protection of the natural environment. We can conserve our environment in the following ways- Walking or riding a bicycle Dumping garbage in the dustbin Planting trees Raising public awareness Reusing of natural resources.
4) Explain the negative impacts of soil pollution on human health.
Ans: Soil pollution is the contamination of soil with harmful things. Effects of soil pollution are decreased soil fertility, and death of plants and animals. People may get sick with various diseases including cancer by taking those foods grown in polluted soil. 5) Why does population growth cause environmental pollution?
Ans: People use different elements of the environment to meet up the demands of the increased population. It results in the change of different elements and pollutes the environment. For example, people are cutting down trees to have cultivable lands so that they can grow more crops. As a result, environment is getting polluted. Besides, to meet up the demand of food for the increased population, excessive amount of fertilizers and pesticides are being used. These chemicals mixing with the rainwater contaminate the surface water.
Water for Life
Chapter-3
Q.1. What is the water cycle?
Ans: The way that water moves all around the Earth as it changes its state is called the water cycle.
Q.2. Give three examples of how we can prevent water pollution.
Ans: We can prevent water pollution in the following ways:
a) Reducing the use of pesticides
b) Trash keep in bin
c) Raising public awareness.
Q.3. Give four ways to get safe water from unsafe fresh water.
Ans: The following ways to get safe water from unsafe fresh water- Filtration Sedimentation Boiling Purifying water with chemicals.
Q.5. What are the three states of water?
Ans: The three states of water are –
a) Ice (Solid)
b) Liquid
c) Water vapour (gas)
3. Descriptive Questions:
Q. 1. Explain why the surface of the glass with ice water gets wet.
Ans: Air contains vapour all the time. We can explain that the surface of glass with ice water gets wet through this experiment. Necessary materials: A glass, few pieces of ice. Procedure: We will take few pieces of ice in water of a glass. The glass becomes cold because of ice which is kept in it. Observation: Reaching cold surface of glass water vapour of the air turns into water drops. So, the surface of the glass gets wet. Result: From this experiment, we can prove that the surface of the glass with ice water gets wet.
Q.2. Explain the process of water cycle.
Ans: The process of water cycle is given below. Evaporation: The water of ponds, canals, rivers and seas turn into vapours by the heat of the sun. Condensation: water vapour rises in the air, it cools down and condenses into tiny droplets. Forming cloud: These tiny droplets of water gather at a place and form clouds. Rainfall: The tiny droplets of cloud unite together and become larger. This large water droplet falls on earth as rainfall. Water of rainfall: Rain water flows over the soil and mixes with river water. Finally river water falls into the sea water. Thus the cycle is completed.
3) Why do animals need water?
Ans:
Water is very essential for living things. Animals need water for the following reasons. Animals need water to survive. Water helps to carry nutrients to all of the body parts. Water helps body to absorb the nutrients. To digest the food. Water maintains proper temperature of the body.
4) How can we explain that water is in the air?
Ans: We know that air contains water vapour. We can explain that water is in the air through this experiment.
Necessary materials: a clear plastic bag and a vessel filled with ice water.
Procedure:
i) We will fill up the plastic bag with air.
ii) Then we will tie the bag tightly.
iii) Now we will put the bag into the vessel.
iv) After some time we will take it out from the vessel.
Observation: When the bag was put in a vessel with ice water, the vapour inside the bag cool down and turned into water.
Result: From this experiment we can prove that water is in the air.
5) How can we get safe water from pond’s water?
Ans: Water of ponds, canals and rivers has mud and dirt in it. We can get safe water from pond’s water by the following ways: By filtration through cloth or filter we can get clean water. But this clean pond water is not free from germs. We can separate clean water from dirty water by depositing sediments at the bottom of a pitcher or pot. This clean pond water is also not free from germs. By boiling both the filtered water and separated clean water we can get safe water.
6. Why are dew and water droplets on the surface of a glass with ice water alike?
Ans: The drops of water that form on cool surfaces such as grass and leaves during winter night are called dew. When the air comes in contact with cold surface of the glass, water vapour turn into water droplets by cooling. Dew of glass or plants and water droplets of a glass with ice water are formed in the same way. So, dew and water droplets on the surface of glass with ice water are alike.
1. What is energy?Ans: The ability to do work is called energy.2. What is matter?Ans: Materials that has weight and takes up space is called matter.3. What is atom?Ans: All matter is made up of very tiny particles that we cannot see with our naked eyes.4. What is molecule?Ans: A molecule is a group that is made up of two or more atoms joined together.5. What is energy transformation?Ans: The change of energy from one form to another is known as energy transformation.6. Give 5 examples of forms of energy.Ans: Forms of energy are heat, light, electrical energy, mechanical, sound.7. How does light travel?Ans: Light is the form of energy that helps us to see. Light travels as radiation.8. What forms of energy does a guitar produce?Ans: The energy that can create different types of light and help us to see is called light energy. Sound comes from light energy from the vibration of objects. Guitar produces sound energy
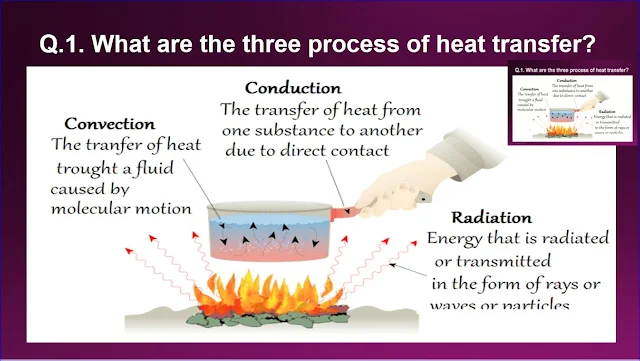
1. Transfer of heat through solid matter is called conduction.
2. Conduction can work through solids.
3. For example, if we place a metal spoon in the hot water, soon it begins to feel hot. This is because the spoon is heated by hot water, and then the heat spreads to the colder end of the spoon
1. Transfer of heat energy through the gases and liquids is called convection.
2. Convection can work through liquids and gases.
3. For example, when we put a pot of water on a stove, the heated water near the bottom of the pot rises to top. At the same time, the cold water near the top sinks to the bottom of the pot and then it is heated and rises to the top. Through this process heat spread from top to bottom of the pot.
1. Radiation is the process in which energy is emitted from a source without any medium.
2. Radiation can even work without any medium.
3. Light is the form of energy that helps us to see. Light travels as radiation.