Environment of Life
1. What is symbiosis? Explain it.
Ans: In the living world existing organic relationship between plants and animals can be designated with the term symbiosis
2. What is plankton?
Ans: The producers are the photosynthetic algae and plants of shallow water. The free-floating microscopic organisms are called plankton.
(There are two main types of plankton: phytoplankton, which are plants, and zooplankton, which are animals. Zooplankton and other small marine creatures eat phytoplankton and then become food for fish, crustaceans, and other larger species.)
3. What is a parasitic food chain?
Ans: Parasitic plants and animals in most of the cases derive their food from a host much larger in size than they are. In some cases other smaller parasites are dependent on all the parasites for their food. In this type of food chain, the primary producers may not be always at the beginning level. The chain remains incomplete.
Man ——> mosquito —–> Dengu Virus
Remarkably, the blood sucked by a female Aedes mosquito does not provide any nutrients to the mosquito but helps to develop its egg inside the body.
4. What is antibiosis?
Ans: If the growth and development of any organism is partly or wholly interrupted by the biochemical substance produced by an other organisms then this process is called antibiosis. This type of relationship mainly found in micro-organisms.
(Antibiosis is a biological interaction between two or more organisms that is detrimental to at least one of them; it can also be an antagonistic association between an organism and the metabolic substances produced by another.)
5. What is mutualism?
Ans: The relationship is mutualism when in the association both the organisms are benefited . For example, a bee, or fly, etc. flies around from flower to flower to attain the nectar and as a result, the pollination is accomplished.
(Mutualism describes the ecological interaction between two or more species where each species has a net benefit. Mutualism is a common type of ecological interaction.)
6. The balance of environment is restored through the interaction and interdependence of different organisms. Explain it.
Ans: The rhizobium bacteria resting at the roots of leguminous plants form nodules, fix atmospheric nitrogen in them. They supply this fixed nitrogen to the host leguminous plant, and in return collect their carbohydrates from it.
Q.7. What is negative interaction among different organisms and the balance of environment?
Ans: Negative interaction can be grouped into three categories, such as-
i) Exploitation:
In this case one organism enjoys its rights by exploiting directly or indirectly another organism from its rights, for example, dodder. A dodder with the help of the absorbing structure hosteria collects food from the plant, which has provided it with shelter. A cuckoo is never able to build a nest. It lays its egg in the nest of a crow, and the crow hatches its egg for it.
ii) Competition:
There may be tough competition between organisms for light, air, water and food. In this competition, the stronger organism survives and the weaker one is abandoned. This is a good example of inter and intra- species struggle of Darwinism.
iii) Antibiosis:
If the growth and development of any organism is partly or wholly interrupted by the biochemical substance produced by an other organisms then this process is called antibiosis. This type of relationship mainly found in micro-organisms.
Creative Questions:
-------> Green insect --------> Carnivor insect
1. Green plants --------> Small bird ----------> Fox
----------> Snail
------------> Rabbit ------> Fox
a) What are decomposers?
Ans: Some microorganisms, like bacteria and fungus, get their food from the waste of plants and animals and their dead bodies, and as a consequence, they are mixed with the soil and water by being decomposed. These mixed components can be again consumed as food components. This is why these microorganisms are called decomposers or transformers.
b) What is a food web? Write in detail.
Ans: In most cases, the same consumer can be placed in different trophic levels. This way some food chains collectively may form a net or web like structure. This is called a food web. This is a phenomenon for both the terrestrial and aquatic ecosystem.
c) In which food chain in the food web mentioned above is the most energy spent?
Ans: In the figure above, biggest food chain is Green plants --------> Green insect ----> Carnivorous fly ------> Small bird -----> Fox.
This food chain has the most trophic level than all food chains in the food web of the extract. Some energy gets wasted in every level of all types of food chain. The green insect does not store that amount of energy, which it procures from the producers green plants. Again the amount of nutrition that a carnivorous fly, consumer of second level obtains from the green insect does not even reach its own body, as some of the energy is released in the inanimate environment.
Energy collected in the green plants more goes out in small bird and fox. This way at the time of transferring food bird and fox. This way at the time of transferring food from one organism to another, much energy goes out of the system in accordance with the principal of ecosystem.
The flow of energy is always unidirectional. This energy flow can never be turned opposite. This is why if in an ecosystem the number of trophic level is greater, energy waste increases accordingly. So, in this food chain in the food web mentioned above is the most energy spent.
d) Analyse what the consequences will be occurred in the ecosystem if the bird in the food chain mentioned above is extinct.
Ans: Only the extinction of a species in an environment may cause a large catastrophe. Stability of the environment biodiversity will be hampered if a species is distinct.
The number of green insects and carnivorous flies will increase, because small birds eat them as their food. If the number of green insects increases, the number of green plant will decrease. Because green insects live by eating plants. So, production of crops will fall. Animal world will hardly alive because shortage of food. On the other hand, presence of oxygen will reduce if number of trees decreases in the ecosystem. Because green plants produce oxygen by photosynthetic process. So, indirectly small birds maintain the balance of ecosystem. Again for, consumer of top level will extinct if small birds which is their food.
So, if the bird in the food chain mentioned above is extinct, environment will become imbalance.
2. a) What is biodiversity?
Ans: Biodiversity is the abundance and variability among organisms existing on the earth.
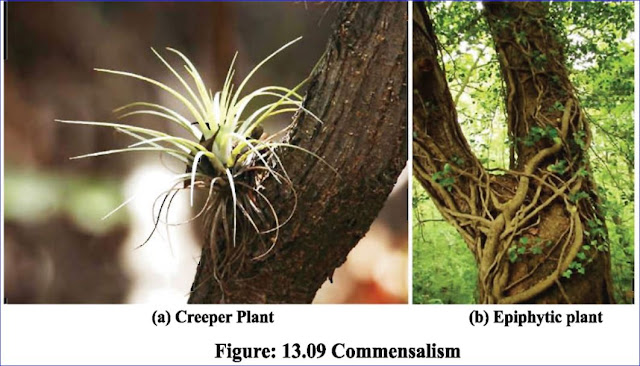
b) Write in detail what you understand by commensalisms.
Ans: Sometimes in the association of two organisms, only one gets benefited. Through the other associate is not benefited, it does not lose anything. This association is called commensalisms. Such as, creeper plant with its root is anchored in the soil and creeps up around a big tree. This way it collects sufficient amount of light by spreading on other plant. Woody creeper doesn't depend on the plant that is providing shelter for it for food and does not do any harm to it.
Epiphytic plants collect food from the air but do not do any harm to the plant providing shelter. Some algae dwell in bodies of other plants, but do not do any harm to them.
c) Explain the causes of difference in temperature in the figure mentioned above.
Ans: The picture mentioned above is of a green house. This is a house made of glass where trees are planted. Green house is built generally in winter based country. the causes of difference in temperature are -
* It heats up because incoming visible solar radiation from the sun is absorbed by plants, soil and other thing inside the building.
* Air warmed by that heat from hot interior surface is retained in the building by the roof and wall. In addition, the warmed structures and plants inside the green house radiate some of their thermal energy in the infrared spectrum, to which glass is partly opaque. So, some of this energy also trapped inside the green house.
Thus, the glass used for a green house works as barrier to air flow and it's effect is the trapped energy. Within the green house. Although heat less due to thermal conduction through the glass and other building materials occurs, net energy and therefore temperature increases inside the green house.
d) analyse the impacts of the reactions caused by the process mentioned in the diagram above.
Ans: Entire world can be compared to green house and excessive carbon dioxide can be worked as green house glass. The green house effect is a processes by which thermal radiation from a planetary surface is absorbed by atmospheric green house and is re-radiation in all direction.
Solar radiation at the frequencies of visible light largely pass through the atmosphere to warm the planetary surface, which then emits this energy at the lower frequencies of infrared thermal radiation. Infrared radiation is absorbed by green house gases (CO2, CO, N2O etc) which in turn re radiate much of the energy to the surface and lower atmosphere. The temperature is raised for enhanced green house gases.
Human activities, primarily the burning of fossils fuels and clearing of forests, have intensified the natural green house effects, causing global warming.
Multiple choice questions:
1. Which one is a saprophytic food chain?
a) grass--------> deer -------> tiger
b) saprophyte ----------> decomposer ------------> Amoeba
c) zooplankton ----------> fish ---------------> hydra
d) green plants -----------> bird --------------> fox
2. Among the animals through commensalisms-
a) one is benefited from the associates
b) though none of the associates is benefited but none is also harmed
c) both of the associates become benefited
Which one of the following is correct?
a) i
b) i & ii
c) ii & iii
d) i, ii & iii
Chapter-2
Grade-5
Q.A. Fill in the blanks.
a) ______________________ is one of the main causes of pollution.
b) Effects of pollution on animals are the destruction of their ___________ and food chains.
c) Many _______________ continues to melt and results in sea _______________.
d) Air pollution is the addition of harmful gases, dust particles, smoke or ____________ into the air.
e) Smoke emitted from burning ____________.
2. Short Q/A
Q.1. What is the environmental pollution?
Ans: Our environment changes in many ways. When the changes are harmful to the living things, it is called environmental pollution.
Q.2. What are the effects of air pollution?
Ans: The effects of air pollution are—
i) Global warming
ii) Acid rain
iii) Respiratory diseases like lung cancer, bronchitis etc.
Q. 3. Write down the ways of environmental pollution?
Ans: The ways of environmental pollution are-
Q.4. What are the sources of environmental pollution?
Ans: The main sources of environmental pollution are the burning of fossil fuels, industrialization, population growth, toxic chemical and household waste.Q.5. Write the five ways of environmental conservation.
Ans: The five ways of environmental conservation are- Wise use Dumping garbage in the dustbin Planting trees Raising public awareness Reusing of natural resources.3. Descriptive Answer questions.
1) Explain the harmful effects of environmental pollution.
Ans: The harmful effects of environmental pollution are- Destruction of their habitats Animals get extinct Sea level rise Global warming People sick with lung cancer, respiratory diseases.2) What is noise pollution? What is the harmful impact of noise pollution.
Ans: Noise pollution is sound in the environment that harms the health of human or animal life. Noise pollution has severe mental and physical effect on human health. Depression, hearing loss, sleep disruption and loss of productivity are caused by noise pollution.3) What is environmental conservation? How can we conserve our environment?
Ans: Environmental conservation is the sustainable and wise use and protection of natural environment. We can conserve our environment in the following ways- Walking or riding a bicycle Dumping garbage in the dustbin Planting trees Raising public awareness Reusing of natural resources.4) Explain the negative impacts of soil pollution on human health.
Ans: Soil pollution is the contamination of soil with harmful things. Effects of soil pollution are decreased soil fertility, death of plants and animals. People may get sick with various disease including cancer by taking those foods grown in polluted soil.5) Why does population growth cause environmental pollution?
Ans: People use different elements of the environment to meet up the demands of the increased population. It results in the change of different elements and pollutes the environment. For example, people are cutting down trees to have cultivable lands so that they can grow more crops. As a result, environment is getting polluted. Besides, to meet up the demand of food for the increased population, excessive amount of fertilizers and pesticides are being used. These chemicals mixing with the rain water contaminate the surface water.















Comments