AQA GCSE Chemistry - 2018 Higher Tier Paper-1
1. Soluble salts are formed by reaching metal oxides with acids.
1.1. Give one other type of substance that can react with an acid to form a soluble salt.
Ans: metal
1.2. Calcium nitrate contains the ions Ca²+ and NO₃-
Give the formula of calcium nitrate.
Ans: Ca(NO₃)₂
1.3. Describe a method to make pure, dry crystals of magnesium sulfate from a metal oxide and a dilute acid.
Ans:
- Use magnesium oxide and sulfuric acid
- Add sulfuric acid to a beaker
- Warm sulfuric acid
- Add magnesium oxide
- Continue adding until magnesium oxide is in excess
- Using a filter paper and funnel
- Heat solution in an evaporating basin
- Leave to crystallise
2. This question is about metals and metal compounds.2.1. Iron pyrites is an ionic compound.Figure -1 shows a structure for iron pyrites.
Determine the formula of iron pyrites.Use Figure 1.Ans: Fe S 2
2.2. An atom of iron is represented as 56/26 FeGive the number of protons, neutrons and electrons in this atom of iron.
Number of protons 26Number of neutrons 30Numbers of electrons 26
2.3. Iron is a transition metal.
Sodium is a Group 1 metal.
Give two differences between the properties of iron and sodium.
1. iron has a high melting
2. iron is less reaction
Nickel is extracted from nickel oxide by reduction with carbon.
2.4. Explain why carbon can be used to extract nickel from nickel oxide.
Ans: *carbon is more reactive
* carbon will displace
2.5. An equation for the reaction is:
NiO + C ➡ Ni + CO
Calculate the percentage atom economy for the reaction to produce nickel.
Relative atomic masses (Ar) C = 12 Ni = 59
Relative formula mass (Mr) : NiO = 75
Give your answer to 3 significant figures.
59/87 x 100
= 67.8 %
Percentage atom economy = 67.8 %
3. Chemical reactions can produce electricity.
3.1. Figure 2 shows a simple cell.
Which of these combinations would not give a zero reading on the voltmeter in
Figure 2?
Tick one box.
Electrode A Electrode B Electrolyte
Copper Zinc Sodium chloride solution
Alkaline batteries are non-rechargeable.
3.2. Why do alkaline batteries eventually stop working?
Ans: a reactant is used up
3.3. Why can alkaline batteries not be recharged?
Ans: The reaction is not reversible
Hydrogen fuel cells and rechargeable lithium-ion batteries can be used to power electric cars.
3.4. Complete the balanced equation for the overall reaction in a hydrogen fuel cell.
2 H₂ + Ο₂ ➡ 2 H₂Ο
3.5. Table 1 shows data about different ways to power electric cars.
Table 1
Hydrogen fuel cell Rechargeable
lithium-ion battery
Time taken to refuel or 5 30
recharge in minutes
Distance traveled before
refueling or recharging in miles Up to 415 Up to 240
Distance traveled per unit of energy in km 22 66
Cost of refueling or recharging in £ 50 3
Minimum cost of car in £ 60,000 18,000
Evaluate the use of hydrogen fuel cells compared with rechargeable lithium-ion batteries to power electric cars.
Use Table 1 and your own knowledge.
From the table (fuel cells could be judged as better)
* time for refueling a fuel cell is faster than recharging.
* a fuel cell has a greater range.
* From other knowledge
* Hydrogen can be renewable if made by electrolysis using renewable energy.
* Lithium-ion batteries can catch fire
* Produces only water.
From the table ➡ lithium-ion uses energy more efficiently
* Cost of lithium-ion car much less.
* Cost of recharging much less than refueling with hydrogen
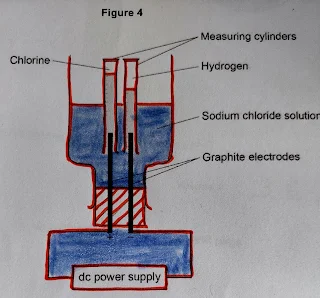
4. A student investigated the electrolysis of sodium chloride solution.
Figure 4 shows the apparatus.
The student measured the volume of gas collected in each measuring cylinder every
minute for 20 minutes.
4.1. Figure 5 shows the volume of hydrogen gas collected in the measuring cylinder after 8 minutes.
What is the volume of hydrogen collected?
volume = 3.6 cm³
4.2. Which of the lines on Figure 6 show that the volume of gas collected is directly proportional to the time?
Tick one box.
Ans: Hydrogen line only
4.3. Which of the lines in Figure 6 show a positive correlation between the volume of gas collected and time?
Ans: Both lines
5.4. Draw a fully labeled reaction profile for the reaction between zinc and copper sulfate solution in Figure 5.
6. A student investigated the electrolysis of different substances.
Figure 6 shows the apparatus.
6.1. Explain why electrolysis would not take place in the apparatus shown in figure 6.
Ans: solid does not conduct
ions can move in liquid
6.2. Explain why graphite conducts electricity.
Answer in terms of the structure and bonding in graphite.
Ans: * each carbon
* one electron per carbon is delocalised
* these electrons move through the structure