Co-ordination
1. What is a phytohormone?
Ans: The biochemical substance which is produced in the plant body and regulates the growth and development of the plant, is called a hormone. Plant hormone is called phytohormone. The main natural phytohormones are auxin, gibberellin, cytokinin, abscisic acid and ethylene.
2. What is gravitational feeling?
Plants respond directly to Earth’s gravitational attraction, and also to light. Stems grow upward, or away from the center of Earth, and towards the light. Roots grow downward, or towards the center of Earth, and away from light. These responses to external stimuli are called tropisms. Plants’ growth response to gravity is known as gravitropism; the growth response to light is phototropism. Both tropisms are controlled by plant growth hormones.
Biology for 9 & 10
3. What is the nervous system?
The nervous system coordinates with different organs and systems, carries impulses to different parts of the body, and maintains a relation with the environment by responding to stimuli.
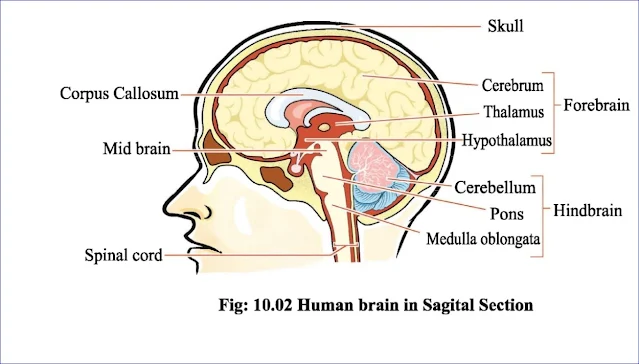
4. What constitutes the central nervous system?
Ans: Central nervous system consists of the brain and the spinal cord.
5. What are the causes of paralysis?
Loss of sensation and motion in a part of the body is termed paralysis. Generally a stroke is the cause of paralysis. Neck or spinal cord injury or accidents may also be the cause of paralysis. Nerve disease, damage of spinal cord may also be the cause of paralysis.
6. Discuss the role of hormones in the growth of plants.
Ans: Auxin and other hormones help in growing roots in graft tissue. In the presence of light, the hormone auxin becomes inactive and so, in the dark, the concentration of auxin increases. The growth of the lighted part, being inhibited, turns more towards the light.
7. What are the symptoms of thyroid problems?
Ans: A deficiency of thyroid hormones creates an obstruction in mental development. It causes rough skin and distinct facial features.
Multiple-choice questions
1. What hormone is secreted by the thymus gland?
a. Thyroxine
b. Parathyroxine
c. Thymoxine
d. Thyrotrapine
2. Islet of langarhans –
i) help in carbohydrate metabolism
ii) secretes insulin hormone
iii) controls metabolism of the body
Which one is correct?
a) i
b) i & ii
c) ii & iii
d) i, ii & iii
On the basis of the following diagram answer the questions 3 and 4.
3. Which one of the following is applied to ‘A’.
a. Phototropism
b. Geotropism
c. Hydrotropism
b. Chemotropism
4. Which one of the following is applicable in the development of part A:
a. Auxin
b. Gibberellin
c. Cytokinin
d. Abscisic acid
Creative questions
1. Ohona observes different types of plants at an agricultural farm. She notices some small seedlings kept in electrical light in a cold room. She also observes that flowering is not occuring in some fruit, trees and some fruits being immature are falling off the trees.
a. What is a biological clock?
Ans: The co-ordination of light and dark in the plants is called biological clock.
b. What is vernalization?
Ans: The acceleration of flowering of plants by applying chilling on them is called vernalization. Flowering is prolonged if the wheat of winter is cultivated in summer. If 2 – 5 degrees temperature is applied on the seeds after sowing, the normal flowering occurs in them. This process is known as vernalization.
C. What are the causes of the problems found in the fruit trees mentioned in the stem above?
Flowering depends on some aspects. Such as continuous light. The fruit trees in the stem may be did not get the necessary continuous light. That means the fruit plant may be long day plant but they are planted in short day. For this reason flowers did not bloom at this time.
Besides, such as florigen and vernalin. Florigen transforms the vegetative buds into floral buds. Vernalin also helps in flowering.
In the fruit plants of the stem flowering did not occurred because hormones like florigen and vernalin were not created.
Another problem of the fruit trees is that immature fruits are falling off the tree. Some hormones are created in plant body that helps in falling of leaves, flowers, fruit etc. Some of these hormones are abscisic acid and ethylene mainly. Due to excessive acid or ethylene in the root of the small fruits the immature fruits fall off.
d. Explain the causes of keeping the seedling in the environment notices.
In agricultural farm the farmers kept little seedlings in a cold room where a light was on. To get more profit the farmers kept the plants in such an environment with an intention to get fruits in advance. Flowering in plants depend on continuous light mostly.
Again light has a role in the growth of the plants and in making of branches. In perfect growth and branched plant flowering occurs more. The light kept in the room in the cold room.
The acceleration of flowering of plants by applying chilling on them is called vernalization. Due to vernalization in the frontal part of embryo of the plants a role in flowering or fruit production.
So the plants seen by Ohona were kept in such an environment with an intention of advance flowering. By this farmers will do more profit.
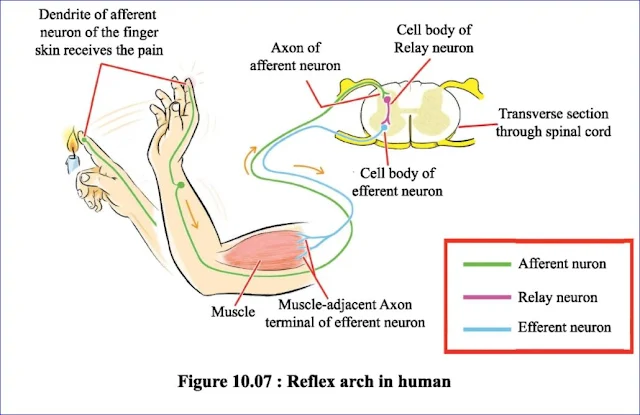
2. a. What is a reflex action?
Ans: The immediate response to a specific stimulus is not controlled by the spinal cord instead of the brain is called reflex action.
b. What is a hormone?
The biochemical substance which is produced in the plant body and regulates the growth and development of the plant is called a hormone.
C. Explain the role of part ‘A’ to create stimulation in human body.
The figure of the stem is neuron. To receive impulse from sensory organs and then work accordingly is the work of neuron. The A marked part is dendrite. The small branched part around the cell body is dendrite. An axon of neuron is connected with a dendrite of a neuron. By this way more than one neuron is connected and forms nervous system. Between the two adjoining nervous there is a bridge or tiny gap between axon of a neuron with the dendrite of the other called synapse. Sensory neuron receives stimulation by the receptor and transmit it to the brain then send off motor impulses to effector. By this stimulation is created in human body. Here the ‘A’ part of dendrite connects with the axon of the next nerve cell and forms synapse to nervous system. If there would no dendrite there would be no synapse and there would be no stimulation in human body. So in human body the importance of part ‘A’ or dendrite is immense.
d. The structure and nature of this cell is different – Analyze it.
The cell of the stem is neuron. It is different from the normal animal cell. The differences are written below-
a. The nerve cell is long shaped. But the normal animal cell is egg-shaped or round-shaped.
b. The nerve cell is divided into two parts. Such as cell body and processes. But animal cells cannot be divided into any parts.
c. In nerve cell there are mitochondria, Golgi bodies, lysosome, fat, glycogen, nissel’s granules. But in a normal cell, there are no nissel’s granules and neurofibril.
d. In nerve cell, there are small branched processes around the cell body called dendrite. But in normal cell dendrite is absent.
e. Branches axons are created in the cell body of nerve cell which are much longer than nerve cell which is absent in normal cell.
f. In nerve cell there are nodes of Ranvier in axon. But in normal cell nodes or Ranvier is completely absent.
So the given logics prove that the structure and nature of nerve cell is different from normal cells.
Parkinson disease:
Causes:
Nerve cells produce a substance called dopamine which helps in muscular movement. Due to Parkinson disease, dopamine producing cells are gradually destroyed. Without dopamine, nerve cells become unable to send stimulation to the muscles. So, the muscle loses its effectiveness.
Symptoms :
Treatment:
Diabetes:
Within the pancreas, there are ductless glands called islets of langarhan's. These glands secrete the hormone insulin. Insulin regulates the metabolism of carbohydrates. If the pancreas fails to produce the required amount of insulin, then the level of glucose increases in the blood above the normal level. Then, glucose is released in the urine. This condition is called diabetes mellitus.
Symptoms:
Diagnosis and treatment :
Structure of neuron:
The neuron is made up of two parts
a) cell body:
b) elongated part:
i) Dendron:
ii) Axon:
The terminal end of one neuron does not join directly to the next dendrite of the neuron cell. This junction of two neurons is called the synapse. Nerve impulses are transmitted through axon terminal synapses to neurons by an electrochemical process.
Endocrine gland:
a) Pituitary gland: The pituitary gland or hypophysis is situated beneath the brain. It is the main hormone-producing gland in the human body, because it secretes several hormones.
Thyroid gland:
Parathyroid gland:
Humans have four parathyroid glands which are situated in the posterior part of the thyroid gland.
Thymus gland:
Adrenal gland:
The adrenal glands are located just above the kidneys. Adrenal glands regulate essential metabolic processes. These glands secrete adrenaline hormones.
Islets of Langerhans:
Gonad or reproductive organ:
These glands are situated in the ovary of a female and in the testis of a male. In mature males and females, reproductive organs produce testosterone and estrogen respectively.
Kidney Structure:
The excretory organ of the human body is the kidney. Two kidneys lie at the back of the abdominal cavity, on either side of the vertebral column and the lower part of the ribcage, attached to the back wall. They are red-brown in colour and bean-shaped. The outer side of the kidney is convex, and the inner side is concave, with an indentation called the hilus or hilum. The ureter and renal vein comes out from the hilum and the renal artery enters the kidney. Two ureters arise from each kidney, proceeding downwards to open into the urinary bladder. The funnel-shaped extended part of the ureter is called the renal pelvis.
Kidney are enclosed with a special fibrous membrane, called the renal capsule. Adjacent to the renal capsule is the cortex, and the inner side is the medulla. These regions are composed of connective tissues and blood vessels. each kidney contains a particular type of tubules called uriniferous tubule. Each uriniferous tubule has two parts, the nephron and the collecting tubule. Urine is produced in the nephron and the collecting tubules carry urine to the pelvis.
Blood vessels are closely associated with the nephrons. Each glomerulus is supplied with blood by a branch of the renal artery called an afferent arteriole. The capillaries of hte glomerulus rejoin to form an efferent arteriole. The efferent arteriole leads off to form a network of capillaries running closely alongside the rest of the nephron. Blood from these capillaries flows into a branch of the renal vein.
Function:
A normal adult man expels almost 1500 milliliter urine daily. Urine contains nitrogenous waste products, such as - urea, uric acid, ammonia, creatinine etc. These are harmful to health. The kidney plays an important role in eliminating these waste products.
a) Each nephron of the kidney is continuously producing urine through a complex process.
b) The ureter carries urine to the urinary bladder, where it is stored.
c) The renal vein carries 'clean' blood' away from the kidneys.
d) The kidneys remove urea and other wastes from blood and excrete it in a liquid called urine.
e) The bladder is a bag which stores urine until you go to the toilet.
f) The renal artery carries 'dirty' blood to the kidneys.
g) The sphincter is a ring of muscle which keeps the bladder closed until you go to the toilet.
Q. 1. What is excretion?
Ans: Excretion is the biological process through which harmful nitrogenous waste products produced by metabolic activity are removed from the body.
Q.3. What are the excretory products?