Bioenergetics
Chapter - 4
A. water
Ans: Respiration, which occurs in absence of oxygen , is called anaerobic respiration. That is, in anaerobic respiration, respiratory substances are partially oxidised with the help of enzymes to produce diffesnt types of organic compounds( ethyl alcohol, lactice acid etc), CO2 and a small amount of energy.
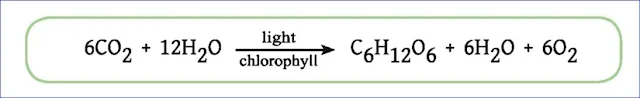
Q.1. What is photosynthesis? Represent it by a chemical equation.
Ans: Green plants produce carbohydrates from carbon dioxide and water in the presence of sunlight. This process is called photosynthesis.
Photosynthasis is a biochemical reaction shown below:
Energy is required to maintain the process of life of organisms, for activities like locomotion, healing of injury, growth and reproduction. The main source of energy is the sun. Through photosynthesis, plants store solar energy in carbohydrates as potential energy. During respiration, this potential energy is converted into kinetic energy (ATP) in the form of heat, which supplies the necessary energy for various physiological activities.
Q.2. What are the raw materials for photosynthesis?
Q.3. What is respiration? Represent it by a chemical equation.
Ans: The process of formation of energy by biological oxidation with the help of oxygen is called respiration. The process of respiration occurs in the cytoplasm and mitochondria of the living cell. However, respiration occurs in all living cells of the plants body, but its rate is very high in case of growing region.
The process of respiration can be illustrated by the following chemical equation:
Ans: The process of formation of energy by biological oxidation with the help of oxygen is called respiration.
The process of respiration occurs in the cytoplasm and mitochondria of the living cell. However, respiration occurs in all living cells of the plants body, but its rate is very high in case of growing region.
The process of respiration can be illustrated by the following chemical equation:
Q.4. State the difference between photosynthesis and respiration.
Q.5. State the difference between aerobic and anaerobic respiration.
The respiration process, which requires oxygen and produces CO2, H2O and a large amount of energy by oxidising the respiration materials completely, is called aerobic respiration.
C6H12O6 + 6O2 ———different enzymes——–> 6CO2 + 6H2O + energy (686 k Cal / Mole)
Respiration which occurs in absence of oxygen, is called anaerobic respiration.
C6H12O6 ————-enzyme—-> 2C2H5OH + 2CO2 + energy (56 k Cal / Mole)
Easy type questions:
Q.1. Explain the dependence of organisms on photosynthesis.
Q .2. Discuss the significance of respiration.
Significance of respiration:
An organism performs all activities with the energy produced through respiration. CO2 released during respiration is used in the process of photosynthesis to produce carbohydrates, the main food of living beings. This process helps plants to absorb mineral salts, which indirectly drive the growth and other physiological activities in a plant. The energy required for cell division is produced through respiration. So, this process also controls the growth of organisms. Different sub-alkaline or organic acids are also produced, through respiration and they help other physiological activities of life. This process is also used in industry. Through this process, lactic acid, through fermentation, produces curd, cheese etc. It is also used in making bread. Yeast produces alcohol and CO2 gas through the process fermentation. CO2 makes the bread rise.
Multiple choice questions:
1. Which one is evolved as a by-product in the process of photosynthesis?
A. water
B. carbohydrates
C. Oxygen
D. Carbon dioxide
Q.2. What number of ATP is produced in the glycolysis stage of respiration?
A. 4
B. 6
C. 8
D. 18
Look at the stem and answer question no. 3 and 4.
3. The functions of both A and B are-
i. To intake O2
ii. To release H2O
iii. To remove CO2
Which one of the following is correct?
A. i & ii
B. i & iii
C. ii & iii
D. i, ii & iii
4. The process accomplished in figure X-
i. Keeps the environment cold
ii. Helps the process of photosynthesis
iii. Inhibits the process of respiration
Which one of the following is correct?
A. i & ii
C. ii & iii
D. i & iii
E. i, ii & iii
Creative questions
Aerobic respiration:
The respiration process, which requires oxygen and produces CO2, H2O and a large amount of energy by oxidising the respiratory materials ( carbohydrates, proteins, lipids, different kinds of organic acids) completely, is called aerobic respiration.
Aerobic respiration is generally divided into 4 distinct stages:
Stage 1 : Glycolysis:
When oxidized through chemical reactions, one molecule of glucose (C6H12 O6) is broken down into two molecules of pyruvic acid (C3H4O3). Four molecules of ATP and two molecules of NADH+H+ are produced in this stage. In this process, no oxygen is required. It is the initial stage for both aerobic and anaerobic respiration. It takes place in the cytoplasm of the cell.
Stage-2: Acetyle Co-A formation:
This stage also takes place in the cytoplasm. Each molecule of pyruvic acid, produced in glycolysis, is transformed into a molecule of 2 - carbon acetyl co-A, a molecule of CO2 and a molecule of NADH+H+.
Stage-3 : Kreb's cycle:
In Kreb's cycle, 2 - carbon acetyle C0- A, are oxidized to produce two molecules of CO2. This cycle is named after the British biochemist Sir Hans Krebs who discovered the cycle. In this stage, acetyl Co- A enters the mitochondria and participates in Kreb's cycle. All the reactions of this cycle occur in the mitochondria. In this cycle, from one molecule of acetyl Co-A, two molecules of CO2. three molecules of NADH+H+, one molecule of FADH2 and one molecule of GTP are produced.
Stage-4 : Electron transport system:
In this stage, NADH+H+ produced in the above three stages are oxidised. Consequently ATP, water, electrons and protons are produced. The energy is released elecrons containing high - energy move through the electron transport system. This energy is used in the formation of ATP. The electron transport system takes place in the mitochondria.
1.a. What is the chemical formula of pyruvic acid?
Ans: The chemical formula of pyruvic acid is C3H4O3.
b. What do you understand by anaerobic respiration?
Ans: Respiration, which occurs in absence of oxygen , is called anaerobic respiration. That is, in anaerobic respiration, respiratory substances are partially oxidised with the help of enzymes to produce diffesnt types of organic compounds( ethyl alcohol, lactice acid etc), CO2 and a small amount of energy.
c. Explain how the component A is being produced.
d. What is the effects on plants if the production of A is inhibited? Explain.
Ans: A of the stem which later arranges essential energy in different chemical reactions. In plant body, at the time of respiration of the stored static energy ATP is released as chemical energy in the form of heat. If energy is required for organic synthesis, conduction and other metabolic activities ADP and AMP are formed by breaking down of ATP and so the energy is produced.
2. Bipasha, a student of class X, likes to eat carrots. As the carrots contains glucose, it provides her with energy. Her younger sister asks her how a plant derives energy for its growth. She replies that a plant also derives energy through the respiration.
A. What is photolysis of water?
Ans: The process in which oxygen, hydrogen and electrons are evolved through the hydrolysis of water with the help of sunlight and chlorophyll is called the photolysis of water.
B. What are C4 plants?
Ans: In C4 plants, both the Hatch and Slack cycle and the Calvin cycle are carried out simultaneously. The rate of photosynthesis in C4 plants is higher than that of in C3 plants. Some examples of C4 plants are maize, sugercanes, other plants of grass type, motha grass and amaranthus.
C. Explain with a chart how much energy is produced in Kreb’s cycle from two molecules of food eaten by Bipasha.
Ans: Carrot serves the necessary energy to Bipasha’s body. To get energy, the glucose which remains in carrot reduces in various stages of respiration. From 2 molecules of glucose, in first stage 4 molecules of pyruvic acid, in second stage 4 molecules of Acetyl co- A and in third stage 12 molecules NADH + H+, 8 molecules of CO2, 4 molecules FADH2 and 4 molecules of GTP can be got which is shown in the table below:
D. What is the effects on plants if the process mentioned
above is inhibited?
Q. 10. In the photosynthesis process where is the main place?
a. Mesophyll tissue
b. xylem tissue
c. phloem tissue
d. Xylem vessel
Q.1. What are the products of the light dependent reactions of photosynthesis?
a. ATP, RuBP and NAD
b. ATP, oxygen and reduced NADP
c. GP, oxygen and NAD
d. GP, reduced NADP and RuBP
Q. 2. Where in the chloroplast are the products of photophosphorylation used?
a. envelope
b. granum
c. stroma
d. thylakoid
Q.3. In separate experiments, an actively photosynthesising plant was supplied with one of two labelled reactants:
water containing the 18O isotope of oxygen
CO2 containing the 17O isotope of oxygen
In which products of photosynthesis would these isotopes be found?
18O
A. O2 produced by chloroplast grana
B. O2 produced by the chloroplast stroma
C. carbohydrate produced by chloroplast grana
D. carbohydrate produced by the chloroplast stroma
17O
carbohydrate produced by the chloroplasat stroma
carbohydrate produced by chloroplast grana
oxygen produced by the chloroplast stroma
oxygen produced by chloroplast grana
4. Explain how the inner membrane system of a chloroplast makes it well adapted for photosynthesis.
b. copy the table below and insert ticks or crosses to show which structural features are shared by a plant chloroplast and a typical prokaryotic cell.
v = structural feature shared; x = structural feature not shared.
structural feature structural feature shared by chloroplast and typical prokyryotic cell
circular DNA
DNA combined with structural protein to form chromosomes
ribosomes about 18 nm in diameter
complex arrangement of internal membranes
peptidoglycan wall
size ranges overlap
5. a. When isolated chloroplasts are placed in buffer solution with a blue dye such as DCPIP or methylene blue and illuminated the blue colour disappears. Explain this observation.
b. Name the compound, normally present in photosynthesis, that is replaced by the blue dye in this investigation.
6. Distinguish between :
a. cyclic and non-cyclic photophosphorylation
b. photophosphorylation and oxidative photophosphorylation
c. the roles of NAD and NADP in a plant
7. a. Draw a simple flow diagram of the Calvin cycle to show the relative positions in the cycle of the following molecules:
CO2 (1C)
GP /PGA (3C)
triose phosphate (3C)
RuBP (5C)
b. Show the point in the cycle at which the enzyme rubisco is active
8. a. Explain what is meant by a limiting factor.
b. List four factors that may be rate- limiting in photosynthesis.
c. At low light intensities, increasing the temperature has little effect on the rate of photosynthesis
At high light intensities, increasing the temperature increases the rate of photosynthesis.
9. a. Copy and complete the table to show the differences between mesophyll and bundle sheath cells in C4 plants. Insert the tick when an item is present in the cell and a cross when it is not.
item Mesophyll cell Bundle sheath cell
PEP carboxylase
rubisco
RuBP
enzymes of Cavin cycle
high concentration of oxygen
light dependent reactions
contact with air spaces
b. Explain what is meant by photorespiration.
10. a. Distinguish between an absorption spectrum and an action spectrum.
b. Pondweed was exposed to each of three different wavelength of light for the same length of time.
For each wavelength, the number of bubbles produced from the cut ends of the pondweed were counted and are shown in the table.
wavelength of light/nm Mean number of bubbles produced in unit time
450